压缩刺激机电特性测试分析评估系统,软骨压缩电位特性测试分析仪
型号:MachOne,
联系人:李先生
联系电话:18618101725
品牌:加拿大BMM
MachOne压缩刺激机电特性测试分析评估系统,软骨压缩电位特性测试分析仪
一、MachOne压缩刺激机电特性测试分析评估系统

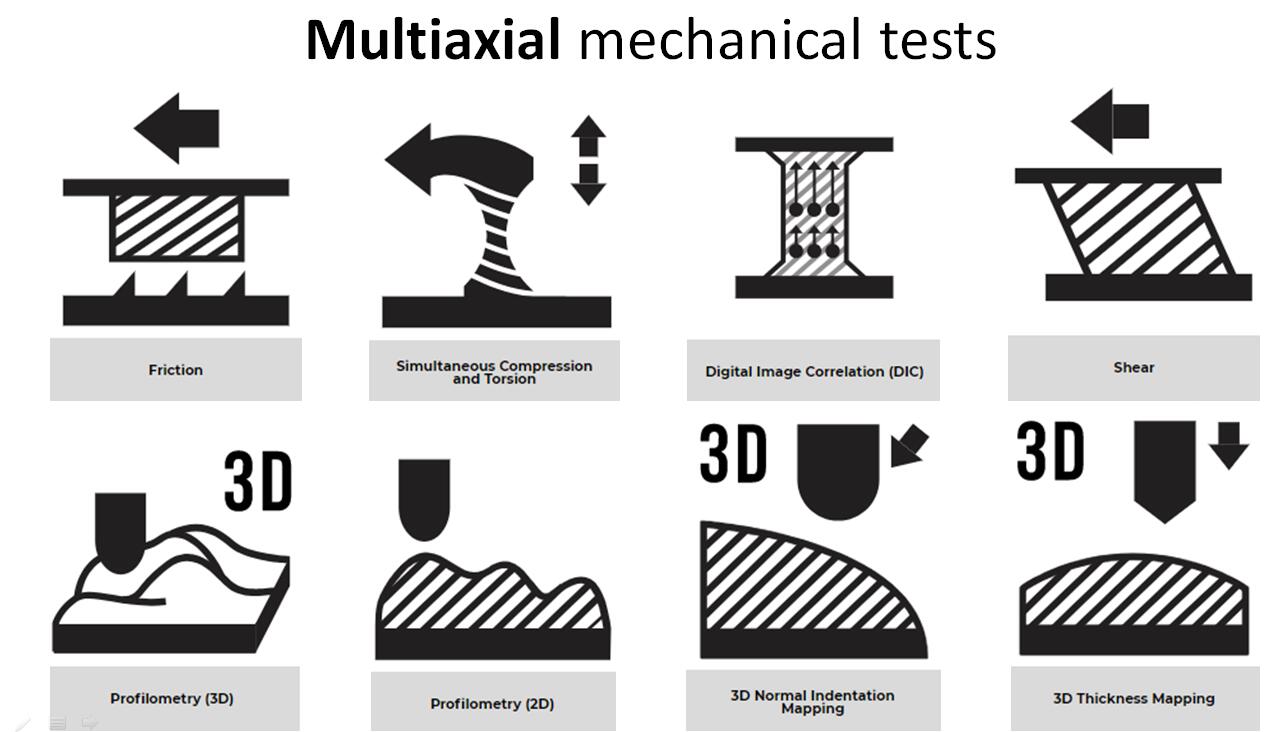
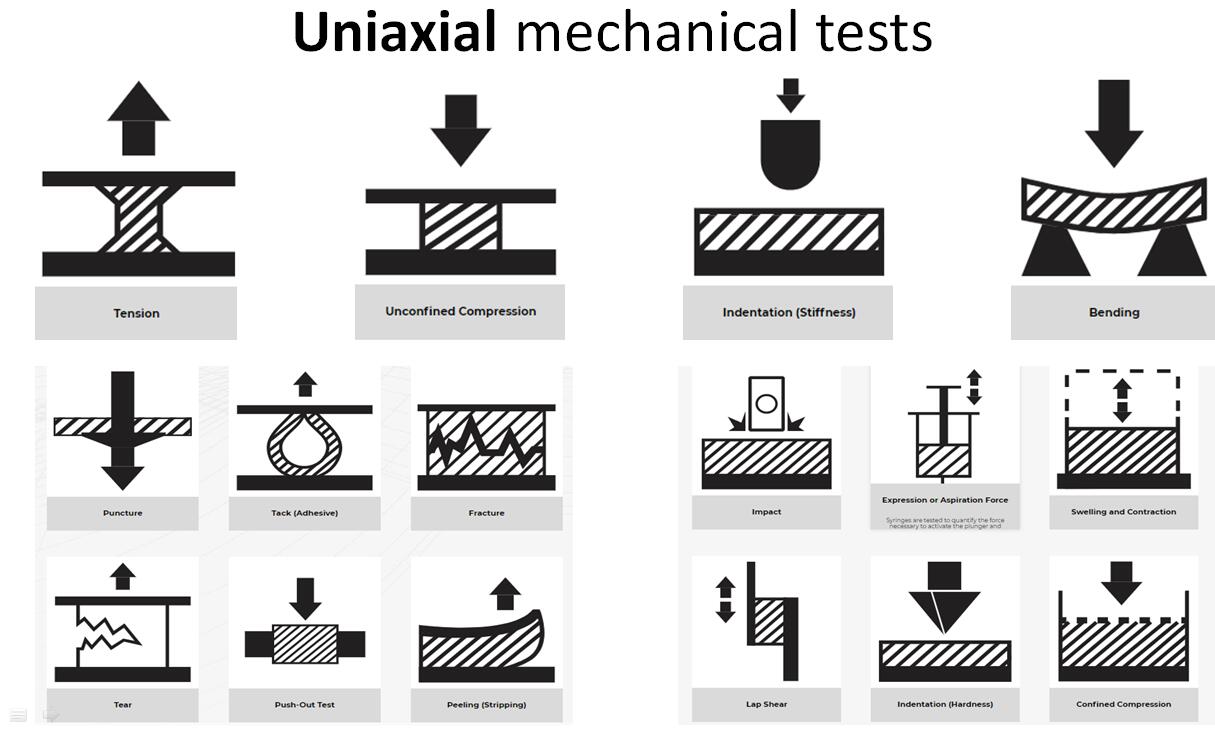
该BMM 材料/组织机电耦合效应特性测试仪(机械力偶联电位测试分析),可带电活性组织或材料进行机械力偶联电位测试分析,比如关节软骨、带电水凝胶等活组织压缩期间同步进行电位测试,可集成3D轮廓表面形貌表征、拉伸、压缩、三弯曲、四点弯曲、扭力、剪切、摩擦磨损、电特性等各种力电多物理场测试。 能对极软、极硬组织材料进行精密可靠的机械刺激和表征。允许表征的机械性能包括刚度、强度、模量、粘弹性、塑性、硬度、附着力、肿胀和松弛位移控制运动各种机械特性
特点
1、适用样品范围广:
1.1、从骨等硬组织材料到脑组织、眼角膜等软组织材料
1.2、从粗椎间盘的样品到j细纤维丝
2、通高量压痕测试分析
2.1、三维法向压痕映射非平面样品整个表面的力学特性
2.2、48孔板中压痕测试分析
3、力学类型测试分析功能齐
模块化集成压缩、张力、剪切、摩擦、扭转、穿刺、摩擦和2D/3D压痕、3D表面轮廓、3D厚度等各种力学类型支持。
4、高分辨率:
4.1、位移分辨率达0.1um
4.2、力分辨率 达0.025mN
5、 行程范围广:50-250mm
6、体积小巧、可放入培养箱内
7 、高变分辨率成像跟踪分析
8、多轴向、多力偶联刺激
9、活性组织电位分布测试分析
10、产品成熟,文献量达 上千篇
|
纤维丝张力和扭力测 |
自动法向压痕和厚度映射 |
胫骨三维轮廓测试 |
机电活性材料(如结缔组织、带电水凝胶等)压缩过程中电位分布 |
可对材料将对机械刺激提供电响应测定分析,例如压电晶体。 也可对生物材料(水凝胶)和组织(关节软骨)表现出机电行为机型测定分析。 然而,在他们的情况下,这是由于流体流经固定带电分子网络(非压电)所致。 在机械刺激期间测量电活性材料的电响应可以提供有关其性质的详细信息。,还可以在电刺激后诱发机械反应。
通过在安装在MachOne上的机电测试腔室中加入一组电极来评估软骨的机电性能,于各种测试方案,包括应力松弛、正弦位移和不同配置下的蠕变(受限和非受限压缩、张力、压痕和弯曲)可测定软骨和半月板两种结缔组织的机电特性。由于组织刚度和压缩产生的电场(或流电位)对组织的生化成分敏感,测试仪与一组电极耦合,可以j确测量这些电信号。研究正常和退化结缔组织的生化成分和机电特性等。
活性材料(如结缔组织、带电水凝胶等)压缩过程中同步测量机电的电位分布
1、(机电测试腔室)ELECTROMECHANICAL TESTING CHAMBER
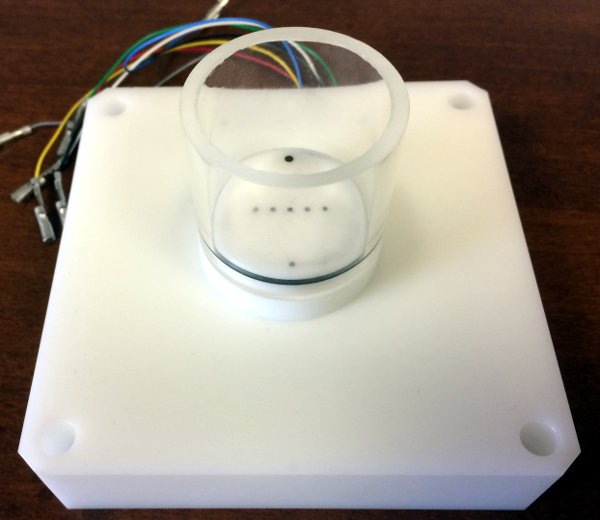

软骨、带电凝胶等压缩期间同时进行机电特性测,该室有5个不同的Ag-AgCl电极通道和一个较大的参比电极。药室可装满PBS溶液
方便清洁和消毒的设计,部坚固可保持其多年的完整性,用于与生理盐水接触,易于组装,并安装在透明材料制成的测试仪上
机电测试腔室的规格:
材料:Ag-AgCl(电极)
直径:1 mm(电极)
间距:4 mm(中心到中心)(电极)
应用案例:
结缔组织机电特性的表征.1部分:关节软骨
在本研究中,使用MachOne型力学测试仪测定了软骨和半月板两种结缔组织的机电特性。由于组织刚度和压缩产生的电场(或流电位)对组织的生化成分敏感,测试仪与一组电极耦合,可以j确测量这些电信号。本研究的目的是建立正常和退化结缔组织的生化成分和机电特性(刚度和流电位)之间的联系。部分主要研究关节软骨。
由于关节软骨细胞外基质主要由带负电荷的蛋白多糖组成,包埋在胶原网络中,因此在液体中存在过量的移动正电荷。软骨的压缩通过分离与固定的带负电的蛋白多糖相关的带正电的移动离子产生流电位。
配对的牛软骨/骨盘(直径3 mm)在有或wu降解剂(白细胞介素-1或白细胞介素-1)的情况下培养11天。
通过在安装在MachOne上的测试室中加入一组电极来评估软骨的机电性能。MachOne设计用于各种测试方案,包括应力松弛、正弦位移和不同配置下的蠕变(受限和非受限压缩、张力、压痕和弯曲)。在这项研究中,用8个直径为50μm、间距为300μm的铂电极组成的线性阵列,在wu侧限压缩几何结构中测量组织表面的流动电位。电极1至6覆盖1.5 mm软骨盘半径,电极7和8位于浴中软骨的外部。试验箱已装满加生理盐水。在2μm/s、20μm的小步压缩序列中施加100μm的静态压缩偏移量,在1、0.1和0.01hz的频率下进行动态正弦测试,位移幅度分别为8、4和2μm,通过在复域中添加每个通道来构造流电位径向分布。用二甲基亚甲基蓝染料和分光光度法测定培养皿中蛋白多糖或糖胺聚糖(GAG)的含量和培养过程中丢失的含量。
图3显示了培养过程中软骨盘中GAG的含量。培养1、4、7和11天后,IL-1处理的培养皿分别损失了10%、20%、65%和75%的GAG含量。MachOne易于使用,其模块化软件允许直接和快速分析动态正弦测试结果。图4显示培养11天后,IL-1处理的椎间盘的动态刚度比对照组低3倍。
应力松弛试验结果分析表明,培养结束时,退化圆盘的静态刚度比对照(0.3mpa)低4倍。图5显示了正常和退化软骨培养11天后的流电位分布。我们观察到IL-1处理的外植体在培养开始后的一天,其周边的电位梯度比对照降低了一半。培养7d后,退化圆盘中心的电位波幅明显低于对照外植体。
MachOne型机械测试仪与电极阵列相结合,可j确测定大范围正常和退化结缔组织的机电特性。
结缔组织机电特性的表征.2部分:弯月面

在本研究中,使用MachOne型力学测试仪测定了软骨和半月板两种结缔组织的机电特性。由于组织刚度和压缩产生的电场(或流电位)对组织的生化成分敏感,测试仪与一组电极耦合,可以j确测量这些电信号。本研究的目的是建立正常和退化结缔组织的生化成分和机电特性(刚度和流电位)之间的联系。研究的二部分是半月板。
半月板是一种类似软骨的组织,但较软,电荷较少。在这种情况下,样品从不同的指定区域被切割成5个3毫米的圆盘(大约1-2毫米厚)。测量了wu侧限压缩下的动刚度和流势分布。值得注意的是,半月板的流动电位大约是软骨的10倍(参见本案例研究的1部分)。这些结果还表明,与中间区域(盘3和5)相比,半月板内部(盘1和盘2)软骨表面的动态刚度和流动电位分布更高。这些结果与半月板蛋白多糖含量有直接关系。
MachOne型机械测试仪与电极阵列相结合,可j确测定大范围正常和退化结缔组织的机电特性。
二、型号的活体在体软骨等压缩流动电位测试评估系统
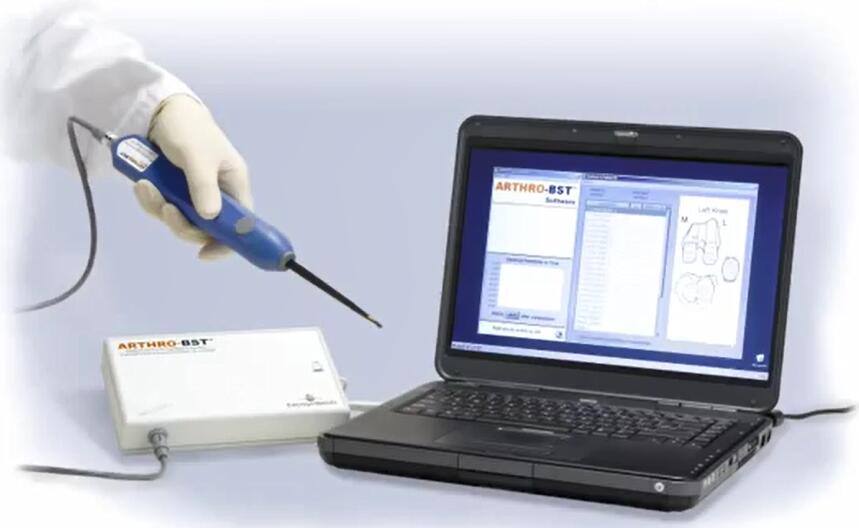
是一种手持式医疗设备,设计用于关节镜手术,以评估关节软骨的功能特性。 通过压缩软骨表面,测量流动电位并计算反映软骨健康状态的定量参数。
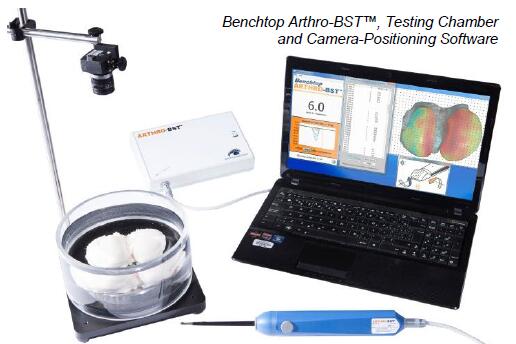
Benchtop 可对关节软骨进行j确的wu损评估。 它计算了一个定量参数,反映了每个测量部位的关节软骨的生化成分和承重特性。 它是为有兴趣仅在离体关节软骨上使用该工具的研究人员开发的。 提供非wu菌一次性吸头,可配备配备高分辨率相机和相机定位软件的测试室,用于绘制大型骨软骨样本。
软骨研究
Benchtop 在软骨修复领域提供了大量研究机会。 它非常宝贵:- 了解软骨疾病,包括软骨退化的潜在原因
- 开发新的治疗产品和软骨修复技术
- 可靠的骨关节炎动物模型的概念
- 创建各种物种的参考映射
工作原理:
台式测量关节软骨的压缩诱导的流动电位。在温和压缩软骨表面期间使用压头测量这些电信号(参见下图)。te的压头设计包括覆盖有37个微电极阵列的球形表面。
该装置计算软骨机电活动的定量参数(QP),其对应于当其流动电位的总和达到100mV时与软骨接触的微电极的数量。高QP表示弱机电特性,反之亦然。 QP是可再现的,并且与施加的力和压头取向wu关。
健康的软骨正常流动电位:
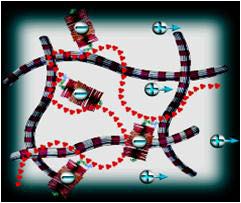
在正常软骨被压缩时,相对于包埋在胶原网络内的带负电荷的蛋白聚糖,间质液的流动取代带正电的移动离子。这产生称为流动电位的电位。
关节炎软骨低流动电位:
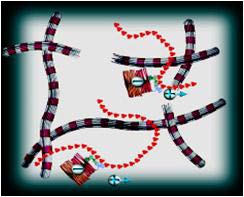
退化的软骨的特征在于蛋白多糖的丧失和胶原网络的减弱。由于相对于带负电的蛋白多糖,正离子的位移较小,因此关节炎软骨的压缩产生异常低的流动电位。

典型测试材料:
OBJECTIVE:The hand-held ™ device is used to map electromechanical properties...Read More