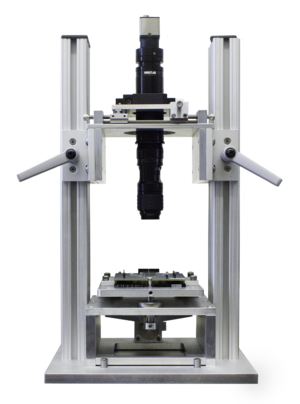
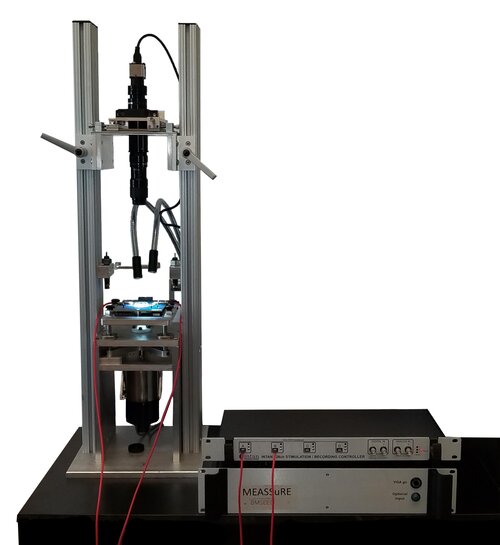
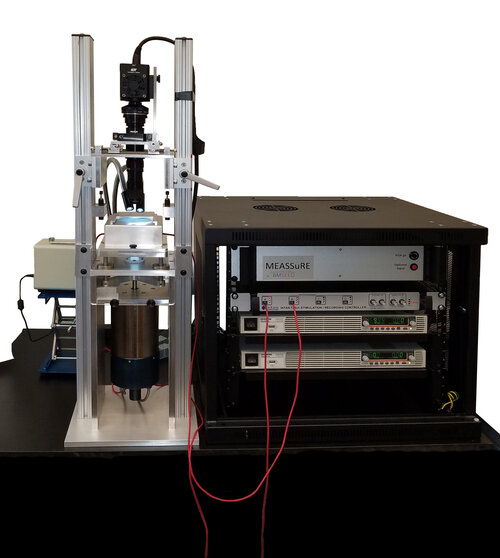
细胞组织电刺激耦合灌流培养观察系统,电刺激耦合灌流,细胞电刺激培养皿
型号:内详
联系人:李先生
联系电话:18618101725
品牌:进口
一、细胞组织电刺激耦合灌流培养观察系统
心肌细胞等在培养的过程中将脱分化,失去其收缩性。可在细胞培养过程中通过给电刺激细胞,来防止其脱分化。电刺激将保持肌细胞的杆状形态及纹状形态。在细胞培养过程中,静态细胞很快就失去收缩功能(6-18小时) 。该系统细胞刺激培养系统可为超过72小时的实验保障的心肌收缩功能。在长达72小时中细胞仍保持蛋白质合成功能,同时细胞保持着正常的氮素平衡。实验时间可以延长到达7天。实验证明,在C-Pace/C-Dish系统能采集到的70%-80%处于良好状态的鼠心肌细胞。使用这个系统就可以进行长达几天的实验并扩大细胞的质量,并且这种系统可以用在任何一种动物细胞上。
特点:
低成本可重复使用
在带有温控的典型装置
适用于大多数流行的显微镜载物台
底部透明,便于实时观察分析
适合任何刺激
可进行耦合灌流
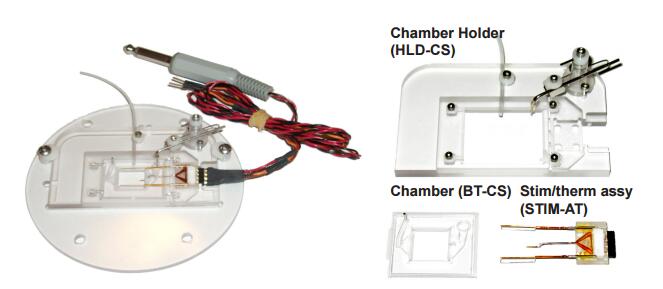
二、经济型铂依电j刺激培养皿


1)可以实时观察实验细胞状态
细胞培养小室是透明的,在实验过程中可以实时观察细胞的状态。
2)培养小室可以放入CO2培养箱,避免了污染,提供了环境
培养小室可以放入CO2培养箱,电刺激控制器连接在外面,不仅可以避免污
染,还可以保证温度和湿度。
三、美国BM公司的细胞组织微电j阵列拉伸刺激与成像记录系统
该细胞组织微电j阵列拉伸刺激与成像记录系统使研究人员能够可重复且可靠地研究生理和病理机械拉伸对生物组织电生理的影响。该系统集成:(1)细胞拉伸设备;(2)电生理数据采集系统;(3)活细胞成像系统三种功能。每个模块都可以作为立工具使用
该细胞组织微电j阵列拉伸刺激与成像记录系统是研究人员以机械方式拉伸细胞/组织,对其进行光学成像以及单/同时记录/刺激电生理活动的完整解决方案。
细胞、组织拉伸功能:
★双轴,单轴
★自定义应变场
★一种快速冲动拉伸或周期性拉伸
★高达50%的应变
★应变速率高达80 / s
★任何拉伸图案
★高重复性
成像功能:
★拉伸之前,期间和之后
★2MP分辨率下每秒高达2,000帧
★定制,易于使用的软件可立测量组织应变
电生理学功能:
★电j同时细胞/组织伸展
★伸展前,伸展中和伸展后记录/刺激
★拉伸前后电生理活动的比较(标准化)
★弹性硅树脂基材上的软MEA
★可以在硬质基材上使用标准MEA
|
型号1
|
型号2
|
型号3
|
|
1)力学模块:应变速率高达1/s,应变度高达20%
2)成像模块:帧率:150fps |
1)机械模块:应变率高达50/s,应变度高达50% |
1)力学模块:应变速率高达80/s,应变度高达80% |
应用范围:
●生理拉伸 |
应用范围:
●病理拉伸 |
应用范围:
●病理拉伸 |
应用文献(Publications):
O Graudejus, T. Li, J. Cheng, N. Keiper, R.D. Ponce Wong, A.B. Pak, J. Abbas, The effects of bending on the resistance of elastically stretchable metal conductors, and a comparison with stretching. Applied Physics Letters, 2017, 110, 221906
W. H. Kang, W. Cao, O. Graudejus, T. Patel, S. Wagner, D. Meaney, B. Morrison III, Alterations in Hippocampal Network Activity after In Vitro Traumatic Brain Injury, Journal of Neurotrauma, 2015, 32(13), 1011-1019
O. Graudejus, Z. Jia, T. Li, S. Wagner, Size dependent rupture strain of elastically stretchable metal conductors, Scripta Materialia, 2012, 66, 919-922
O. Graudejus, B. Morrison, C. Goletiani, Z. Yu, S. Wagner, Encapsulating elastically stretchable neural interfaces: yield, resolution, and recording/stimulation of neural activity, Advanced Functional Materials, 2012, 22, 640-651
J. Jones, O. Graudejus, S. Wagner, Elastically stretchable insulation and bi-level metallization and its application in a stretchable RLC circuit, Journal of Electronic Materials, 2011, 40(6), 1335-1344.
O. Graudejus, P. G●rrn, S. Wagner, Controlling the morphology of gold films on poly(dimethylsiloxane), ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2010, 2(7), 1927-1933
S. P. Lacour, S. Benmerah, E. Tarte, J. FitzGerald, J. Serra, S. McMahon, J. Fawcett, O. Graudejus, Z. Yu, B Morrison, Flexible and stretchable micro-electrodes for in vitro and in vivo neural interfaces, Medical & Biological Engineering Computation, 2010, 48(10), 945-954 (Special Issue)
Z. Yu, O. Graudejus, C. Tsay, S. P. Lacour, S. Wagner, B. Morrison, Monitoring hippocampus electrical activity in vitro on an elastically deformable microelectrode array, Journal of Neurotrauma, 2009, 26(7), 1135-1145
O. Graudejus, Z. Yu, J. Jones, B. Morrison III, S. Wagner, Characterization of an elastically stretchable microelectrode array and its application to neural field potential recordings, Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2009, 156(6) P85-P94