相关产品
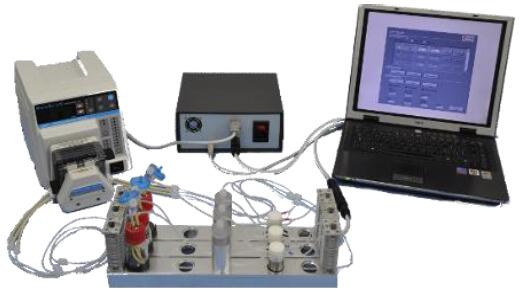
三维灌流培养系统大
型号:内详
价格:请致电:010-67529703
品牌:意大利,美国,瑞士
一、意大利品牌意大利多通道三维细胞组织灌注流培养系统
2.特点介绍
(1). 系统配有9个灌流通道,并且每个都相互立
(2). 系统可以双向灌注
(3). 用户可自定义流量,方向和时间
(4). 系统不同的型号支架,用户可根据需求选取,操作灵活
(5). 流速控制范围广泛,0.1 - 6.0 ml/min范围内均可使用,并可j确控制
(6). 应用范围广泛,统te别适合骨、心脏组织圆柱形片段的长期培养
(7). 可以设置多组实验,每次可以单停止一条灌流通路。
(8). 系统配有光学,非侵入性传感器,可以对pH和培养基中的氧浓度进行实时监控。
(9). 锁有的材料都具有生物兼容性且均经过wu菌处理。
3.应用范围
多通道三维细胞组织灌注流培养系统采用可控、双向、间质灌流,通道多达9个,并且相互立,且系统锁有材料都具有生物兼容性且均经过wu菌处理,应用范围广泛,是普通流体研究的里想系统,另外te别适合骨、心脏组织圆柱形片段的长期培养。
应用案例:Effect of Perfusion Culture System on In Vitro Osteogenesis of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells seeded on Porous Hydroxyapatite
通过激光共聚焦扫描显微镜观察,灌流培养比静态培养得到更好的骨骼组织,且没有改变细胞的活性和扩增能力。
激光共聚焦扫描显微镜检测结果显示灌流培养比静态培养的细胞组织中含有更高的骨钙蛋白的量,产生更均匀、更真实的骨骼组织。
文献:Saino E, Bloise N, Spinelli L,Effect of Perfusion Culture System on In Vitro Osteogenesis of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells seeded on Porous Hydroxyapatite.
4.主要参数
培养小室wu菌内部放入支架,支架尺寸:
支架尺寸:8 [mm] x h 2 [mm] 灌流直径: 6 [mm]
8 [mm] x h 4 [mm] 灌流直径6 [mm]
10 [mm] x h 2 [mm] 灌流直径 8[mm]
10 [mm] x h 4 [mm] 灌流直径 8[mm]
12 [mm] x h 2 [mm] 灌流直径 10[mm]
12 [mm] x h 4 [mm] 灌流直径10 [mm]
培养基储液瓶:
进口(倒钩接头)
出口(倒钩接头)
采样/培养基换端口(鲁尔锁定接头)
0,22 um过滤器端口(鲁尔锁定接头)
蠕动泵:
流速:0.1 - 6 [ml/min]
管道尺寸:ID 1/32"
多可连接9通道,可有控制器控制
控制器:
配备3种不同的控制器:ACE,基于PC版和基于定时器的版本。
光学传感器:
配备pH和O 2光学传感器,通过串联连接在液流回路。
5.参考文献
(1). Modular perfusion bioreactor--
(2). AutoFeed Automatic medium exchanger
(3). Saino E, Bloise N, Spinelli L, Mantero S, Martinetti R, Imbriani M and Visai L. Effect of Perfusion Culture System on In Vitro Osteogenesis of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells seeded on Porous Hydroxyapatite. TERMIS EU meeting Granada 2011.
(4). M. Scavone, N. Bloise, E. Saino, L. Spinelli, L. Fassina, S. Mantero, R. Martinetti, L. Visai. Three-Dimensional Perfusion culture of osteosarcoma cell line (SAOS-2) by bidirectional flow. SIB 2010 Camogli
Quasi Vivo Cell Culture Flow Systems,Quasi Vivo三维灌流培养系统
型号:Quasi Vivo
价格:请致电:010-67529703
品牌:kirkstall
Quasi Vivo® Cell Culture Flow Systems
TRL, now Lonza, is the sole distributor of the Quasi Vivo® Interconnected Cell Culture System in the United States and
Canada. After ten years of research, Kirkstall Ltd. released the Quasi Vivo® advanced cell culture system to provide ‘in-vivo’ like conditions for cell growth. By providing flow of cell culture media the system provides a more physiologically accurate representation than cultures grown in static well plates.
Kirkstall Ltd. released the Quasi Vivo® advanced cell culture system to provide ‘in-vivo’ like conditions for cell growth. By providing flow of cell culture media the system provides a more physiologically accurate representation than cultures grown in static well plates.
The Quasi Vivo® system consists of a series of cell culture chambers connected through dynamic flow of media throughout the system. This arrangement allows more in-depth studies of interactions between cell types, and supports meso-scale culture systems to provide more physiologically relevant metabolic data not available with conventional in-vitro techniques.
Introducing…Quasi Vivo® – Advanced Interconnected Flow Systems
Watch the video below for a 5-minute introduction to Quasi Vivo®, a commercially available Milli-fluid interconnected cell culture system that is flexible, easy to use and provides a significantly more human relevant research environment.
- Pharmaceutical
- Biotechnology
- Chemical
- Cosmetic
- Academic Research
Webinar
Watch the archived webinar “Building Better In Vitro Models Using the Quasi Vivo® System”, for a proper introduction to Quasi Vivo®. Dr. Kelly Davidge, Kirkstall, discusses the many applications of Quasi Vivo®, with a particular focus on Liver, Cardio and Co-culture models
Quasi Vivo® Products

QV500
The QV500 cell culture chamber provides a flexible research tool for low-flow perfusion cell culture. Molded from medical grade silicone, the QV500 is compatible with monolayer cultures using glass and plastic coverslips as well as a range of scaffolds to support 3D cell culture models.

QV600
The QV600 Air-Liquid Interface (ALI) chamber has been designed to culture skin, respiratory epithelium, and other tissues requiring membrane support using commercially available standard 24 well hanging inserts. The QV600 can also be adapted to create a double cavity chamber to study membrane and barrier models.

QV900
The QV900 6-chamber optical tray is a compact, disposable unit which provides a range of configuration options within the footprint of a standard well-plate. The QV900 tray is made of cell culture treated polypropylene and each chamber is the diameter of a standard well of a 24-well cell culture plate.

Pumps
TRL can supply two quality peristaltic pumps ideal for working with theQuasi Vivo® system:
-
- Parker Polyflex 6-channel peristaltic pump: 6 parallel channel peristaltic pump. Compatible with humidified incubators, manual control. Power supply accepts any voltage 100-240V.
- Parker Polyflex 2-channel peristaltic pump: 2 independently controlled pump heads, compatible with humidified incubators, manual controls, dimensions (cm) h:10.5, w 19.5, d 17. 100-120V power.
Accessories
We carry the components necessary to replace used parts.
Quasi Vivo® Product Catalog
| QuasiVivo® Catalog Number | Description |
| QVCWSK | Quasi Vivo® QV500 Culture-well starter kit (inc. 3 QV500 chambers, tubing, and reservoirs) |
| QVCW5X | 5-pack of Quasi Vivo® QV500 culture-well chambers |
| QVTWSK | Quasi Vivo® QV600 Trans-well Starter Kit (inc. 3 QV600 chambers, tubing, and reservoirs) |
| QCTW5X | 5-pack of Quasi Vivo® QV600 trans-well chambers |
| QV6WSK | Quasi Vivo® QV900 6-well starter kit (inc. 3 Quasi Vivo® QV900 6-well trays, tubing, and reservoirs) |
| QVT12X | 12-pack of Quasi Vivo® QV900 6-well trays |
| QVT24X | 24-pack of Quasi Vivo® QV900 6-well trays |
| QVT60X | 60-pack of Quasi Vivo® QV900 6-well trays |
| QV6WTU | Sterile connecting tubing for Quasi Vivo® QV900 6-well trays |
| QVPP6C | Parker Polyflex 6-channel peristaltic pump |
| QVPP2C | Parker Polyflex 2-channel peristaltic pump |
| QVRESB | Reservoir Bottle |
Only Available in North America.
Visit the Lonza e-store to place your order online or contact Customer Service at (800)638-8174.
Quasi Vivo® User Manuals
Each manual contains detailed instructions on the use of the corresponding product.
QV500 User Manual
QV600 User Manual
QV900 User Manual
Parker PF 600 Cell Culture Tray User Manual
Additional Resources
“Why Quasi Vivo®?”
A series of short videos with Quasi Vivo® users to find out why they use our interconnected flow system within their research.
A series of short videos with Quasi Vivo® users to find out why they use our interconnected flow system within their research.
A poster that demonstrates how the Quasi Vivo system improves gene expression for many cell types, including hepatocytes.
应用:
生成适合临床前实验的3D细胞支架结构
瑞士,Ucup三维灌流培养系统



-
Organotypic models (Bone remodeling, Tumor microenvironment)
-
3D cell expansion and differentiation
-
Investigation of cell-scaffold interactions
-
Investigation of cell-extracellular matrix interactions
-
Generation of 3D cell-scaffold constructs suitable for preclinical experimentation
Apply instantly your current cell culture concepts and simply let Ucup further extend them by performing the seamless transition to the 3D context.
| Features | Advantages | Benefits |
| Direct perfusion | Unifrom cell seeding | Uniform tissue |
| Efficient nutrition and waste removal | Viable tissue, up to several weeks of culture | |
| Physiological conditions (mimicking inetrstitial fluid flow and associated induced shears | Physiologically relevant tissue | |
| Simple and smart design (patented) | Easy and ready to use | No previous experience with 3D cell cultures required |
| Minimized manual operations | Highly reproducible results | |
| Efficient with many cell types | Versatile cell and tissue culture models | |
| Supple scaffold adaptors | Compatible with a wide spectrum of 3D porous scaffolds of various composition, architecture and sizes | |
| Access to cell culture medium through valves | Suitable to seed and co-culture several cell types, even at different culture time points | Possibility to investigate complex cell-cell and cell-extracellular matrix interaction |
| Efficient cell retrieval from scaffolds after culture (with standard enzymatic treatment) | Easy cell analyses (cytofluorimetry, gene expression etc.) |
Product Configuration
|
1x syringe pump |
1x rack |
10x Ucup disposable bioreactor kits |
1x Starter kit |
|||

|
+ |

|
+ |

|
= |

|
| The driving force of the system. It generates the oscillating fluid flow of the cell/medium suspension. It cannot be purchased separately. | A rotating rack for easy and correct positioning of Ucup disposable bioreactors. It can also be purchased separately. | The central core of the system. It is disposable and it comes with 10x adaptors to fit the specific size of your scaffolds. Scaffolds can also be purchased separately. | It provides all what you need to start your 3D cell cultures. Additional accessories (e.g. forceps, syringes) and testing units are also included. |
If you are convinced of the benefits that a 3D culture environment can provide,the Ucup bioreactor is the essential tool to conduct with your experiments.
For assistance and advice to set up your experiment, do not hesitate to contact CELLEC’s expert team to address your questions.
应用文献:
-
Boccardo and Gaudiello 2016 In this paper, the perfusion-based bioreactor is used for the generation of an adipose mesenchymal stromal cells -based engineered constructs (Title: Engineered mesenchymal cell-based patches as controlled VEGF delivery systems to induce extrinsic angiogenesis, Acta Biomaterials)
-
Cerino 2016 presents an application for engineering an in vitro 3D multi-cellular muscle-like tissue model (Title: Three-dimensional multi-cellular muscle-like tissue engineering in perfusion-based bioreactors, Biotechnology and Bioengineering)
-
Hirt and Papadimitropoulos 2015 demonstrates the importance of perfusion flow in 3D cultures of tumor cells to efficiently mimic functional features observed “in vivo” and to test anticancer compounds (Title: Bioreactor-engineered cancer tissue-like structures mimic phenotypes, gene expression profiles and drug resistance patterns observed in vivo,Biomaterials)
-
Centola 2015 In this study, the perfusion-based bioreactor system is used to improve cartilage digestion, resulting in higher and more reproducible yield of cell populations with high proliferation and chondrogenic capacity (Title: An improved cartilage digestion method for research and clinical applications, Tissue Engineering Part C, Methods)
-
Bao 2015 presents a humanized in vitro model that reduces the need for experimental animal models, while recapitulating key biological events in a periodontal pocket (Title: Establishment of an oral infection model resembling the periodontal pocket in a perfusion bioreactor system, Virulence)
-
Papadimitropoulos 2014 presents an efficient expansion method of mesenchymal stromal cells by direct seeding and culturing fresh bone marrow preparation within the pores of 3D porous scaffold (Title: Expansion of human mesenchymal stromal cells from fresh bone marrow in a 3D scaffold-based system under direct perfusion, PLoS One)
-
Hirt 2014 highlights the potential of perfusion-based models to create 3D tumour microenvironment for cancer immunobiology studies and pre-clinical assessment of innovative treatments (Title: In vitro 3D models of tumor-immune system interaction, Advance Drug Delivery Review)
-
Papadimitropoulos 2013 presents an application/method for seeding open porous rapid prototyped polymeric scaffolds (Title: A collagen network phase improves cell seeding of open-pore structure scaffolds under perfusion, Journal of Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine)
-
Sadr 2012 presents an application/method to generate a decellularized cell-laid extacellular matrix which enhances the biological performance of polymeric materials (Title: Enhancing the biological performance of synthetic polymeric materials by decoration with engineered, decellularized extracellular matrix, Biomaterials)
-
Gueven 2011 presents an application for upscaling osteogenic and vasculogenic grafts (Title: Engineering of large osteogenic grafts with rapid engraftment capacity using mesenchymal and endothelial progenitors from human adipose tissue, Biomaterials)
-
Papadimitropoulos 2011 presents an application for engineering an in vitro bone organ model (Title: A 3D in vitro bone organ model using human progenitor cells, European Cell & Materials)
-
Di Maggio 2011 a review for our approaches to engineering in 3D vitro niches (Title: Toward modeling the bone marrow niche using scaffold-based 3D culture systems, Biomaterials)
-
Santoro 2010 presents an application for upscaling cartilaginous grafts (Title: Bioreactor based engineering of large-scale human cartilage grafts for joint resurfacing, Biomaterials)
-
Scherberich 2007 presents an application for generating osteogenic and vasculogenic grafts (Title: Three-dimensional perfusion culture of human adipose tissue-derived endothelial and osteoblastic progenitors generates osteogenic constructs with intrinsic vascularization capacity, Stem Cells)
-
Wendt 2006 describes the system for maintaining living uniform tissues in the scaffolds (Title: Uniform tissues engineered by seeding and culturing cells in 3D scaffolds under perfusion at defined oxygen tensions, Biorheology)
-
Braccini 2005 presents an application for generating osteogenic grafts (Title: Three-dimensional perfusion culture of human bone marrow cells and generation of osteoinductive grafts, Stem Cells)
-
Wendt 2003 describes the principle of the Ucup and its impact on cell seeding (Title: Oscillating perfusion of cell suspensions through three-dimensional scaffolds enhances cell seeding efficiency and uniformity, Biotechnology and Bioengineering)